OPTOELECTRONIC PROTECTIVE DEVICES
First-class protection in any environment: optoelectronic protective devices - modern, reliable and equally protective for man and machine.

RELIABLE PROTECTION FOR YOUR INDUSTRIAL REQUIREMENTS:
OPTOELECTRONIC PROTECTIVE DEVICES
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF
OPTOELECTRONIC PROTECTIVE DEVICES?
Optoelectronic protective devices offer several advantages over other protective devices:
FLEXIBILITY
These protective devices are extremely flexible and can be adapted to different applications. They are particularly suitable for monitoring access to machine entrances and exits as well as large hazardous areas.
FAST RESPONSE TIME
Optoelectronic protective devices detect interruptions in the protective field area in fractions of a second. This enables a very fast response to minimise hazards.
PRECISE RECOGNITION
They offer precise detection of objects and people so that security measures are only triggered if there is an actual danger.
WITHOUT BARRIERS
In contrast to physical barriers such as fences or protective covers, optoelectronic protective devices do not require any structural changes to the machine or workplace. This makes installation and maintenance easier.
EXPANDABILITY
They can be used in combination with other safety sensors, such as emergency stop buttons, and safety controls to provide comprehensive protection for man and machine.
SAFETY STANDARDS
They meet international safety standards and contribute to compliance with legal regulations.
OPTOELECTRONIC PROTECTIVE DEVICES AT A GLANCE
There are different types of optoelectronic protective devices that can be selected depending on the application and the specific requirements. A thorough risk assessment and collaboration with security experts are crucial to making the right choice:
SAFETY LIGHT GRID
- A light grid consists of a series of light beams that are transmitted between a transmitter module and a receiver module.
- The generated beams form an invisible barrier that is constantly monitored. If this barrier is breached, this immediately triggers a safety signal that brings the machine or system to an immediate standstill.
- Light grids are often used to cover larger areas where visibility may be limited.
- In particular, they are used for access protection to prevent people, objects or vehicles from entering the protected area.

SAFETY LIGHT CURTAINS
- A light curtain consists of a vertical or horizontal arrangement of light beams, similar to a curtain of light.
- As with a light grid, a safety signal is triggered if the light beams are interrupted.
- Light curtains are particularly suitable for protection against fingers or hands reaching in.
- They are often used to protect hazardous areas where quick and regular access for operators is required without compromising safety.

.
Optoelectronic safety devices | ||||
Safety light grids | Safety light curtains | Laser scanner | Security cameras | |
| Application purpose | Often used for access protection if there is sufficient space to the danger zone. | Above all, danger zone protection. Access protection if required. | Versatile application for danger zone and access guarding | Versatile, suitable for various machine types and applications. |
| Functional principle | Utilises infrared light beams that form a protective field between the transmitter and receiver. If an object interrupts the beams, a signal is triggered to safely stop the system/machine. | Uses cameras and image processing algorithms to recognize objects and movements. | ||
| Detection range | Limited to the area between transmitter and receiver. | 2D, configurable | Depending on the camera position and setting, can cover a larger area. | |
| Range | Medium range | Medium to long range | Short range | Can offer an extended range depending on the camera and lens. |
| Resolution | Mainly focused on the recognition of human bodies. | Also designed to recognize the fingers (14mm) or hand (30mm). | 2D, high-resolution (the effective resolution decreases with the distance to the scanner. | High resolution, can capture and analyze details. |
| Integration in machines | Easy to integrate into machines, but requires precise alignment. | Simple | Complex | Requires careful positioning and configuration of the cameras. |
| Flexibility in the application | Single or multi-sided danger point protection | Versatile in use | High | Can be used flexibly, even for more complex scenarios with variable shapes. |
| Hazard detection for complex shapes | Body | Finger, Hand | Yes | Better suited for identifying complex shapes and movements. |
| Additional functions | Muting, Blanking | Muting, Blanking | Variety | Additional functions such as object recognition, tracking and more. |
| Maintenance and calibration | Little effort | Little effort | Elaborate | Maintenance and updates of the software are necessary. |
| Costs | Low to medium | Low to medium | Medium to high | Can be more expensive, depending on the complexity of the application. |
| LEARN MORE | LEARN MORE | - | - | |
SECURITY APPLICATIONS
Effective solutions start with comprehensive knowledge of requirements. Thanks to our specific application know-how and many years of experience in our focus industries, we offer a unique perspective on safety-related applications.
OUR APPLICATION KNOW-HOW FOR SAFE OPERATING PROCESSES
MUTING
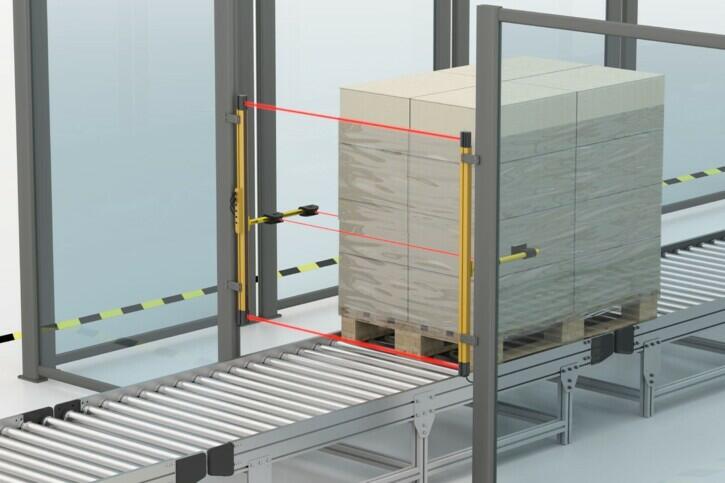

Products used: Light grid with muting function and muting sensors
FLEXIBLE PROTECTION
Muting is a safety function that is used to prevent safety signals from being triggered when objects temporarily enter the protective field of the safety light grid/safety light curtain. Special muting sensors are used in combination with a light grid/light curtain. Muting makes it possible to transport material into and out of the danger zone of a system without stopping the machine and restricting the safety functions.
ACCESS GUARDING
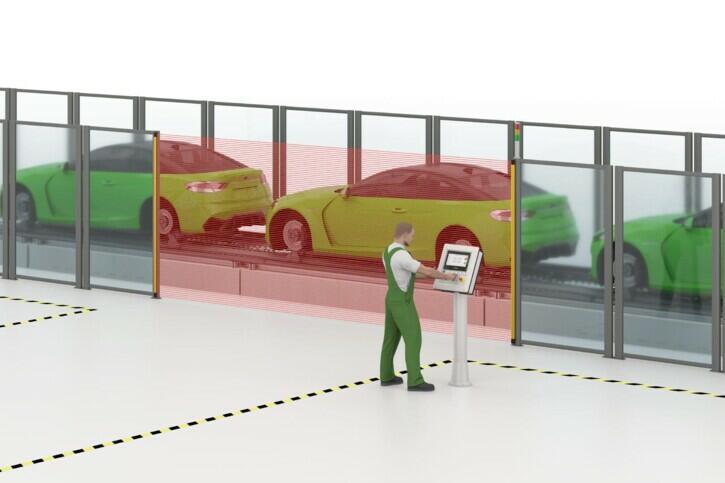
Products used: Safety light grids, safety light curtains
SAFEGUARDING ACCESS AREAS
Optoelectronic protective devices make it possible to safely and reliably monitor access to certain areas of machines or systems. Safety light grids or safety light curtains can be used to safeguard the danger zone and enable the system/machine to be stopped safely in the event of unauthorised access.
AREA PROTECTION
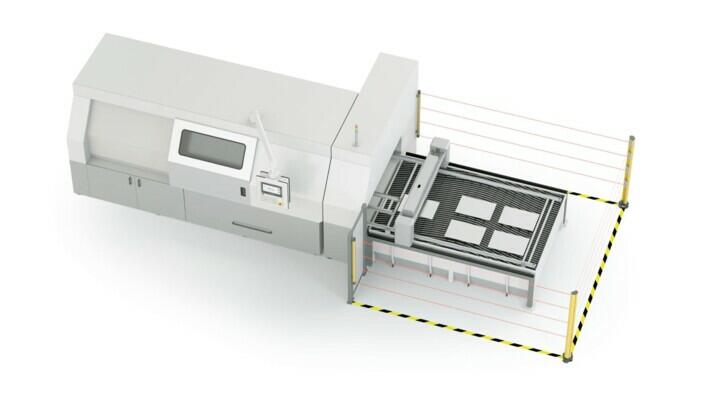
Products used: Safety light curtains, safety laser scanners
SECURING LARGER AREAS
Area guarding focuses on the protection of larger areas or zones in working environments. Safety light curtains or scanners are used to create an invisible protective field. If this field is interrupted, safety measures are triggered immediately.
DANGER ZONE GUARDING
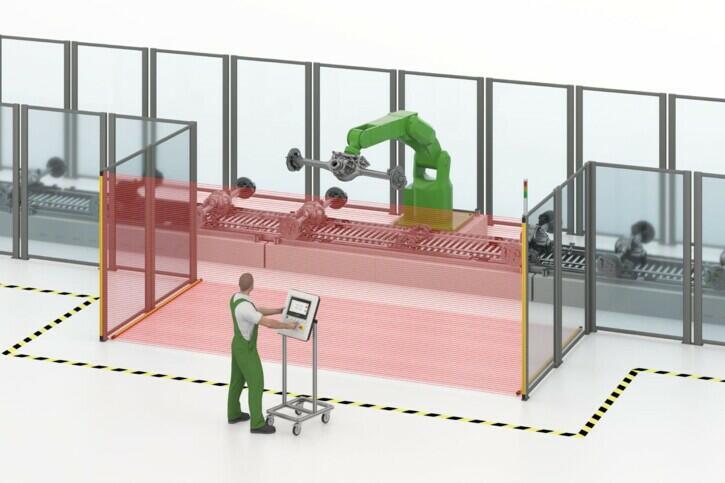
Products used: Safety light curtain, safety laser scanner
SAFETY IN RISK ZONES
Hazardous area protection focuses on protecting zones that are considered particularly risky. Safety light curtains and safety laser scanners are used here in particular. The safety devices ensure that access to these critical areas is monitored and that there is an immediate response if people or objects move into these zones.
POINT OF OPERATION GUARDING
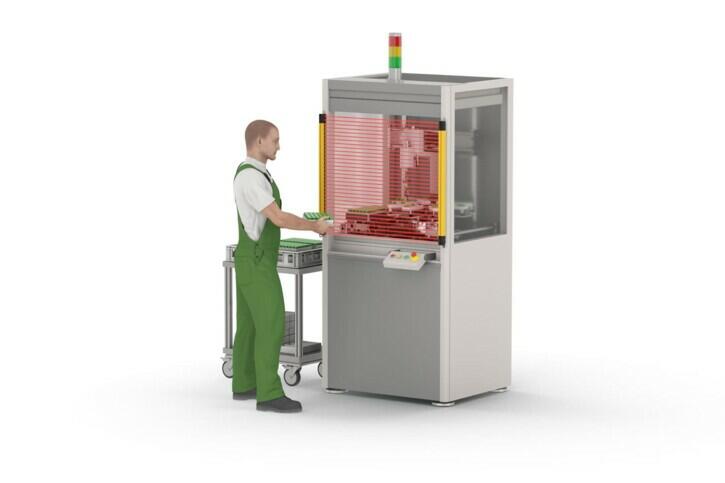

Products used: Safety light curtain, safety laser scanner
PROTECTION AT THE PLACE OF MACHINE OPERATION
This safety application focuses on safeguarding the immediate area in which the machine is operated. Optoelectronic protective devices, such as safety light curtains or scanners, are used to ensure comprehensive protection directly at the operating points. These products help to ensure safe operation directly at the operating points and that machines are stopped immediately in the event of potential risks.
MONITORING OF MATERIAL LOCKS
(MONITORING MATERIAL LOCKS)
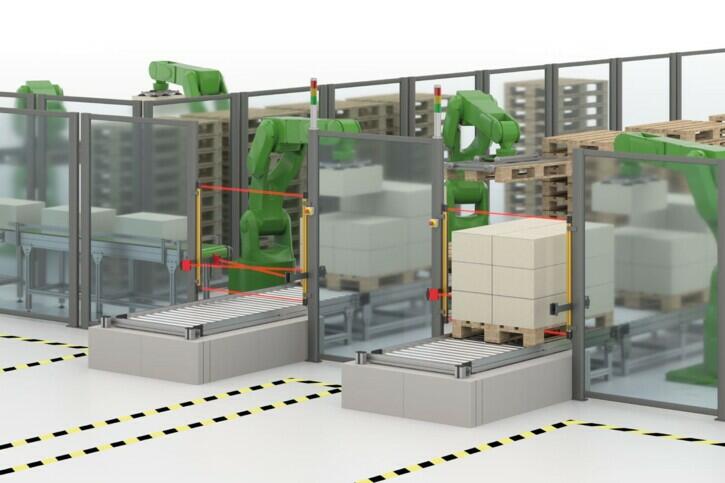
Products used: Safety light curtains, safety light grids, safety laser scanners
PROTECTION AT MATERIAL ACCESS POINTS
The monitoring of material locks is crucial to ensure the safe entry and exit of materials in machines. Optoelectronic protective devices make it possible to monitor material entries and exits in machines. Muting and blanking functions of the safety light grids and safety light curtains allow material to be transported both into and out of the machine through the protective field without stopping the machine. The distinction between people and material ensures safety in this area.
PROVEN EXPERTISE IN OUR KEY INDUSTRY
A STRONG PARTNER FOR MACHINE AND PLANT MANUFACTURERS
Our expertise in the field of functional safety makes us a reliable partner for machine and plant manufacturers. With comprehensive know-how and first-class solutions in the development and integration of safety systems, we help to ensure that your machines meet the highest safety standards.

MAKING MACHINES SAFER -
FOR 20 YEARS
Our long-standing presence with machine manufacturers and operators underlines our commitment to the highest safety standards. We not only offer innovative safety systems, but also comprehensive services to ensure the CE conformity of your machines.

APPLICATION AREAS OF OPTOELECTRONIC PROTECTIVE DEVICES
Optoelectronic protective devices are used in a wide range of industrial and machine applications, especially in applications where the safety of people and machines is the top priority. Some common areas of application are listed below:
✅ LOGISTICS AND MATERIAL HANDLING:
In warehouses, distribution centers and conveyor systems, optoelectronic protective devices are used to ensure the safe transport of goods and materials. They can help to prevent collisions or accidents with forklift trucks, conveyor belts and robots.
✅ AUTOMATED PRODUCTION LINES:
In factories and production facilities, optoelectronic protective devices are used to monitor access to dangerous machine components or areas. They ensure that machines stop or are put into a safe state as soon as a person enters the danger zone.
✅ MACHINE TOOLS:
In the metalworking industry and in workshops where machine tools such as presses and milling machines are used, optoelectronic protective devices ensure the safety of operators by monitoring hazardous areas.
✅ PACKAGING MACHINES:
For machines that package or wrap products, these protective devices are used to ensure that workers do not come into contact with moving parts and injuries are avoided.
SECURITY SOLUTIONS FOR YOUR PERFORMANCE LEVEL
OPTIMALLY PROTECTED IN EVERY SITUATION
A thorough security analysis is essential for meeting specific performance level requirements in various scenarios. The precise selection and integration of these safety devices are crucial to making your project safe and compliant with the applicable safety standards. Our product range offers versatile combination options for our optoelectronic protective devices that are suitable for all requirements and performance levels:

SAFETY CONTROLS
Safety controls are central elements in functional safety. They monitor and control safety functions such as light grids, light curtains and emergency stop systems to ensure that they function properly and react appropriately in the event of danger.

SAFE RELAY
Safety relays monitor safety functions such as the status of light grids and light curtains. They enable circuits to be opened or closed safely in order to minimize hazards.

EMERGENCY STOP SYSTEMS
Emergency stop buttons and switches are crucial safety components that can be used in combination with light grids and light curtains. If a hazard is detected, the emergency stop system can stop the machines or systems immediately, regardless of whether the light barriers are interrupted or not.
THE OPTIMUM COMBINATION
OF SAFETY ELEMENTS FOR YOUR REQUIREMENTS
The selection of suitable safety precautions depends on various influencing factors, such as the type of machine, specific hazards, the parties involved and applicable regulations. A thorough analysis and the consideration of several key criteria simplify the decision-making process:
1. TYPE OF APPLICATION AND MACHINE:
Start by understanding the specific type of machine or system for which you need guards. Each application may have different security requirements.
We recommend:
- Clarify the specific requirements for the machine, e.g:
- How often are interventions in the production process planned?
- Are there entry/exit areas?
- What tasks must the operating personnel fulfil in different operating modes?
- Document the risk assessment and initial risk minimisation measures.
What we offer:
Our experts will support you in preparing the risk assessment. We help you to define the specific danger zones for your application and advise you on possible risk minimisation measures.
2. RISK ANALYSIS AND ASSESSMENT:
Carry out a comprehensive risk analysis. Identify all potential sources of danger and risks that may emanate from the machine. These may include, for example, mechanical and electrical hazards, extreme temperature ranges of components, noise pollution and emissions from the machine.
We recommend:
- Clarify the specific hazards that could occur in the work processes.
- Carry out a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential hazards.
- Document the identified danger zones and their characteristics.
What we offer:
Support in carrying out the risk analysis and assessment.
3. APPLICABLE STANDARDS AND DIRECTIVES:
Make sure you know the current safety standards and regulations that apply to your region and industry. This is crucial to ensure that your security measures meet the required standards.
We recommend:
- Make sure you know the current standards and directives relevant to your machinery.
- We also recommend regular analyses of existing systems in companies with a minimum frequency of five years.
What we offer:
Our experts keep up to date with the latest safety standards and regulations and help you to ensure that your safety precautions comply with current standards.
4. PERFORMANCE LEVEL (PL), CATEGORY AND MTTF:
Based on the performance level determined in the risk assessment, further safety-relevant characteristic values can be calculated that are relevant for your safety concept and the selection of safety-related protective devices.
We recommend:
- Consult both parts of EN ISO 13849 (its counterpart EN 62061) to determine the safety-related parameters.
- When determining the probability of failure, consider not only the quantifiable, calculated safety parameters, but also qualitative factors (behaviour and fault conditions, safety-related software, systematic failures).
What we offer:
We support you in calculating the safety-relevant characteristic values and assist you in drawing up the safety concept.
5. FUNCTIONS AND PROPERTIES:
The risk minimisation measures are defined on the basis of the risk assessment and the safety concept. Optoelectronic protective devices is particularly relevant for material inputs and outputs. In addition to the safety parameters, the product-specific factors are calculated on the following basis: Minimum distance, stopping time, approach speed and penetration distance.
We recommend:
- Rely on the values calculated on the basis of the performance level, such as the average probability of dangerous failure per hour (PFHD), operating time TM and category.
- Also consider the types of approach to the hazardous area: orthogonal approach and parallel approach.
What we offer:
Our experts will help you select optoelectronic protective devices with the desired functions and properties to achieve your safety objectives.
6. INTEGRATION AND INTEROPERABILITY:
Ensure that the selected optoelectronic protective devices are integrated into your machine system in compliance with the relevant standards.
We recommend:
- During installation, ensure that access is only possible through the protective field. It must not be possible to reach under, over or sideways.
- Observe the safety distance resulting from the gripping/entry speed and the stopping time of the hazardous movement.
What we offer:
Our experts support you in calculating the distances, measuring the overtravel distance and advising you on the correct installation.
7. TRAINING:
Don't forget to train your employees. Make sure that they know how to use and maintain the protective devices correctly.
We recommend:
- Clarify the training requirements for your employees who work with the protective devices.
- Plan training courses on the correct operation and maintenance of the safety components.
- Document the training measures.
What we offer:
Wieland offers seminars on the subject of "Inspection of optoelectronic protective devices". In addition to the normative and legal basis for the design and inspection of protective devices, initial and periodic testing is practised.
8. MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION:
Schedule regular maintenance and recurring inspections to ensure that the protective devices are functioning properly.
We recommend:
- Clarify the maintenance and testing requirements for your optoelectronic protective devices.
- Create a maintenance plan and document the checks carried out.
- Document the defects found and the measures taken.
What we offer:
Our experts support you in planning and carrying out maintenance and testing procedures for your optoelectronic protective devices. We ensure that your safety components always function reliably and in accordance with current guidelines and standards.
9. DOCUMENTATION:
Proper documentation is crucial to ensure compliance with safety standards.
We recommend:
- Keep all relevant documentation, such as risk assessments, safety concepts and maintenance logs, up to date at all times.
- This enables seamless tracking of safety measures and makes it easier to identify potential for improvement.
What we offer:
Our experts support you in creating, maintaining and updating your safety documentation. We ensure that your documents comply with current standards and keep an eye on changes so that we can make recommendations for adjustments in good time.

TO THE PERFECT PRODUCT SELECTION WITH OUR ADVICE
The seamless integration of our security products enables the creation of customized security solutions that precisely meet the requirements of your application. Our experts will be happy to advise you on this.
THE MAIN THING IS SAFETY
- WHAT CAN WE DO FOR YOU?
SAFETY-SERVICE

Optoelectronic protective devices and CE conformity:
Concentrate on your core competence while we accompany you through the entire life cycle of your machines - from safety consulting to CE marking.
SAFETY-ENGINEERING

Optoelectronic protective devices for existing systems:
We support you with safety retrofitting. Discover how we can help you make your installations safer and comply with the applicable regulations.
SAFETY TRAINING & CERTIFICATION
FOR THE USE OF OPTOELECTRONIC PROTECTIVE DEVICES

TESTING OF OPTOELECTRONIC PROTECTIVE DEVICES
Our experienced trainers teach the legal and normative principles for the design and correct testing of electro-sensitive protective equipment (ESPE) in the machine safety training course " Testing optoelectronic protective devices". This compact training course on machine safety not only provides you with in-depth theoretical knowledge, but also gives you the opportunity to practice the initial and recurring testing and assessment of the functional safety of optoelectronic protective devices.

IMPLEMENTING OPTOELECTRONIC PROTECTIVE DEVICES (OPD) IN CONFORMITY WITH STANDARDS
Our recent webinar on the effective and compliant implementation of optoelectronic protective devices (OPD) is now available on demand. Gain valuable insights into the latest technologies and best practices for enhancing workplace safety in the industry at your convenience. Learn about the new SLC4 and SLG4 series and access detailed instructions on proper assembly and function testing. Additionally, the webinar covers the importance of over travel measurement and the necessary documentation.
SAFETY STANDARDS & LEGISLATION
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS FOR
OPTOELECTRONIC PROTECTIVE DEVICES
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| EN ISO 13849-1 | This standard describes the safety requirements for the design and integration of safety-related parts of control systems, including the development of software. |
| EN 62061 | This standard specifies requirements for the design, integration and validation of safety-related electronic, electrical and programmable control systems. It is often used as an alternative to EN ISO 13849-1. |
| EN 61496-1 and EN 61496-2 | These standards cover safety requirements and test methods for electrically operated safety light curtains and light grids used to prevent unauthorized access to hazardous areas of machinery. |
| IEC 61508 | This standard deals with the functional safety of electrical, electronic and programmable electronic safety systems. |
| EN 62046 | This standard describes the general requirements for safety light curtains and light grids. |
| EN ISO 13855 | This standard deals with the arrangement of protective devices with regard to the approach speeds of human body parts. |

ADVICE ON SAFETY STANDARDS AND REGULATIONS
If you require detailed information on global safety standards and regulations, we will be happy to assist you. Contact us for comprehensive advice.
DOWNLOAD NOW FREE OF CHARGE!
In a nutshell:
- Standard-compliant integration of electro-sensitive protective equipment (safety light grids and safety light curtains)
- Ensure personal protection in various applications: Single or multi-sided guarding with finger to body detection and monitoring of material airlocks using muting functions
- However, areas monitored by ESPE are only safe if they are correctly installed and regularly checked by manufacturers and operators
- You are on the safe side with the following information
DOWNLOAD NOW!


